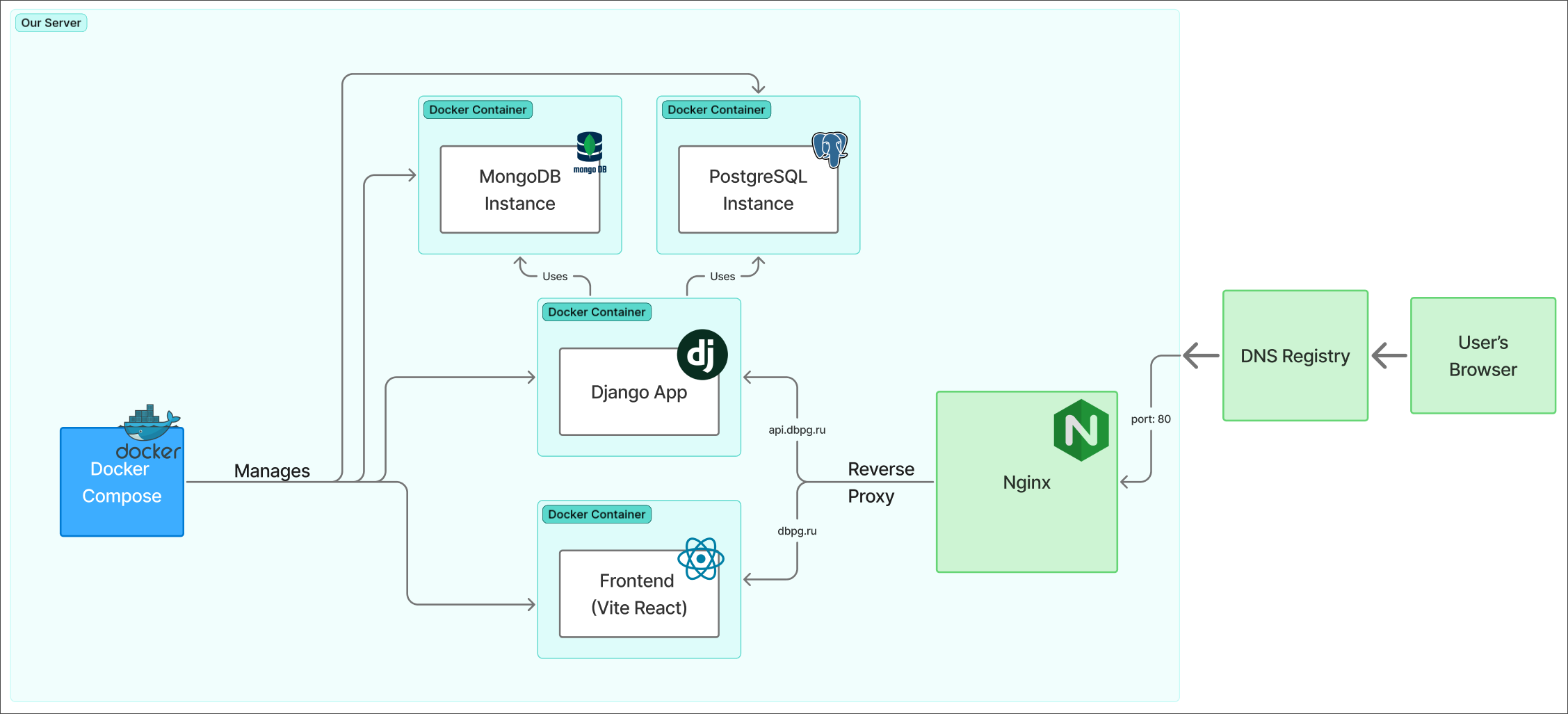
Database-Playground
Architecture
Brief
The architecture is centralized around Templating Model and Database Engines, so let’s go over those concepts briefly
Templating Model
Templates in current implementation of Database Playground - are the snapshots (images) of the database state. So you basically take a photo of your database and save it as template to reproduce that database state later. The template stores the type of database (discussed in Engines part) and the dump (i.e set of queries to run to recreate the state of database on template)
The implementation of templating system is done in backend/core/templates directory and its based on Sessions authentication mechanism for now.
Database Engines
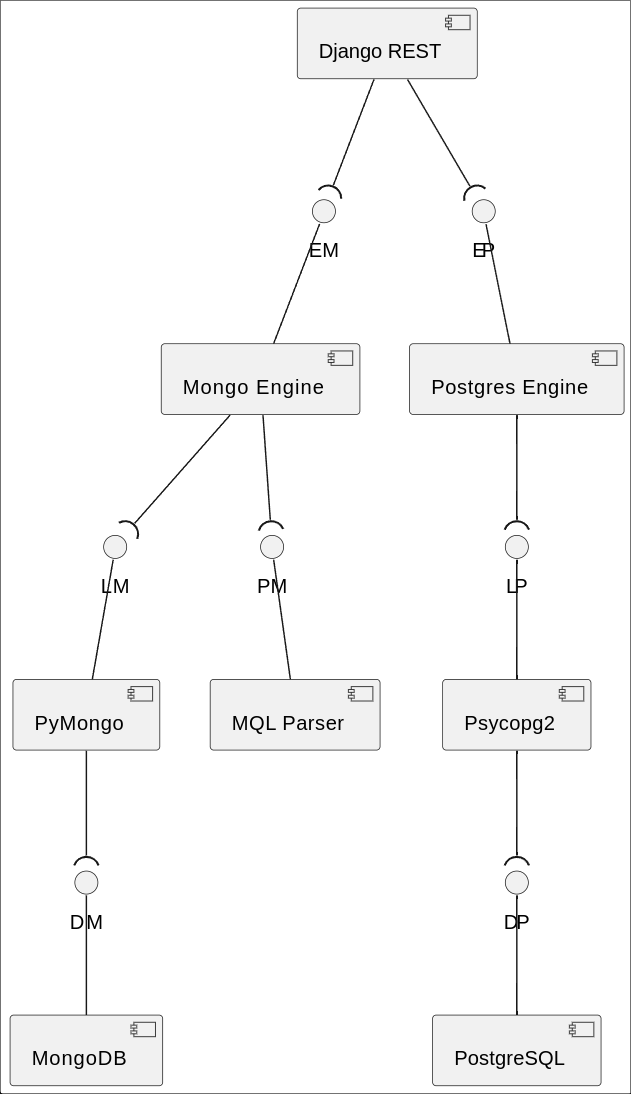
Another important concept is Database Engine - that is a universal API for any database used in Playground (e.g PostgreSQL, MongoDB and even ChromaDB). It proposes similar way of sending queries, returning responses and getting dumps (templates) of the databases. This mechanism makes it really easy to work with different databases in single code space.
The databases of different kind are implemented using unified interface DBEngine.
The examples of these engines are: PostgresEngine, MongoEngine and others later.
You can see implementation of these engines in backend/core/engines directory, while the usage of them (as Django Views) is shown in backend/core/db.
Tech Stack
Backend
- Python
- Django
- Django REST Framework
- Psycopg2
- PyMongo
- PyTest
- Flake8
Frontend
- TypeScript
- NodeJS
- HTML/CSS
- Vite
- React
- React Router
- CSS Modules
- Zustand
- ESLint
- Prettier
Static View
Components of backend
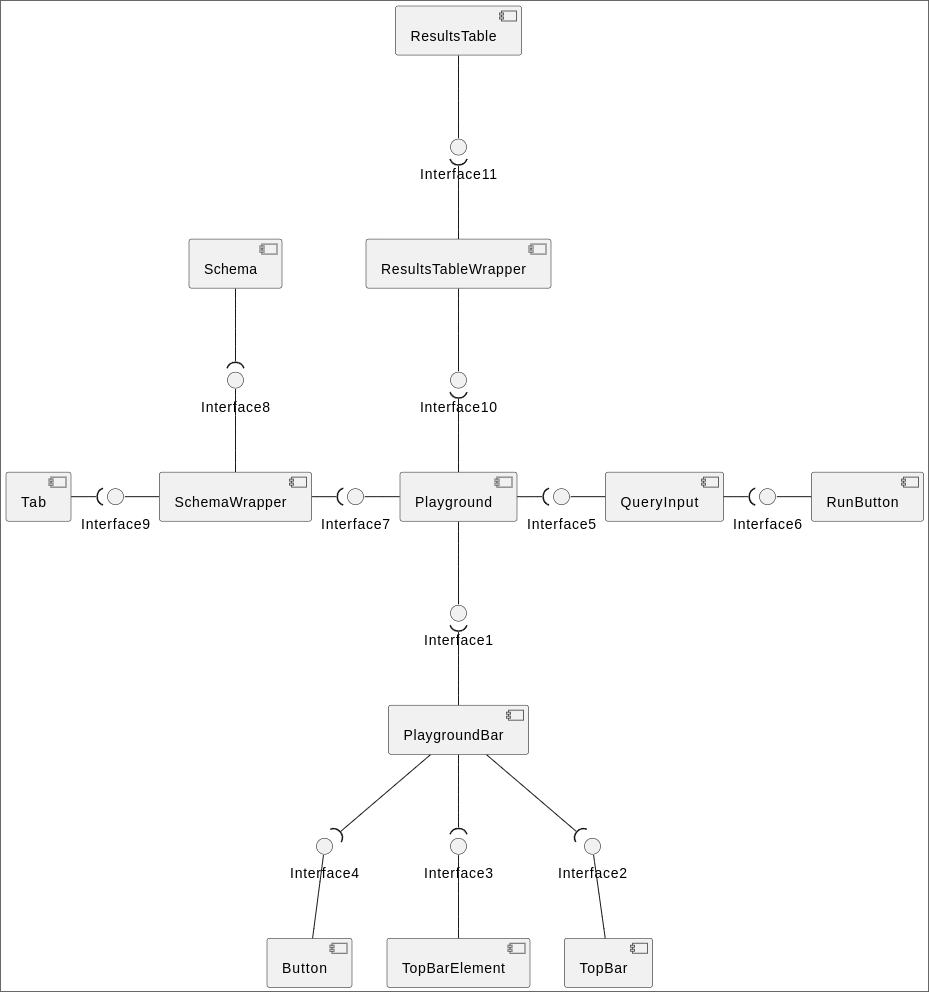
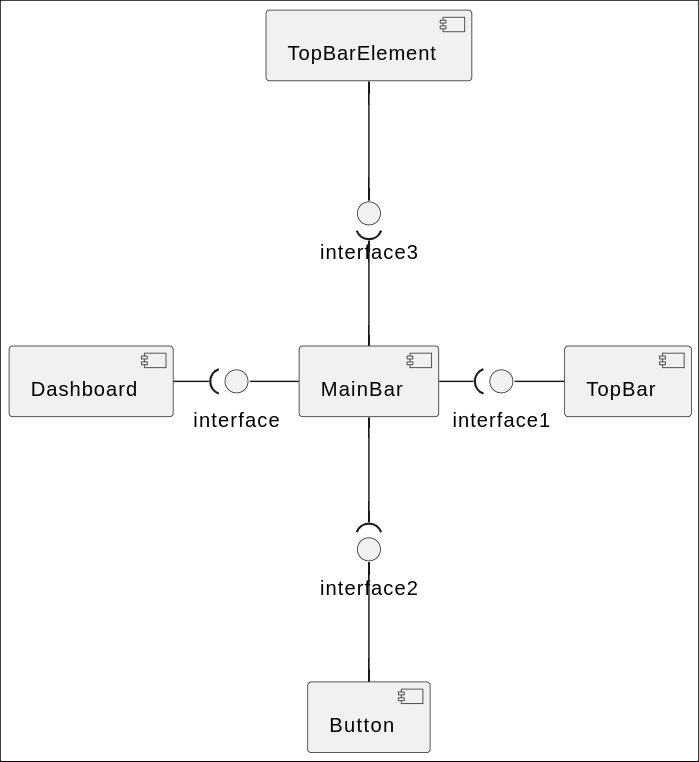
Components of Frontend:
Our frontend architecture uses many small single responsibility components combined togheter. This ensures modularity and reusability in the application.
-
Playground Page
-
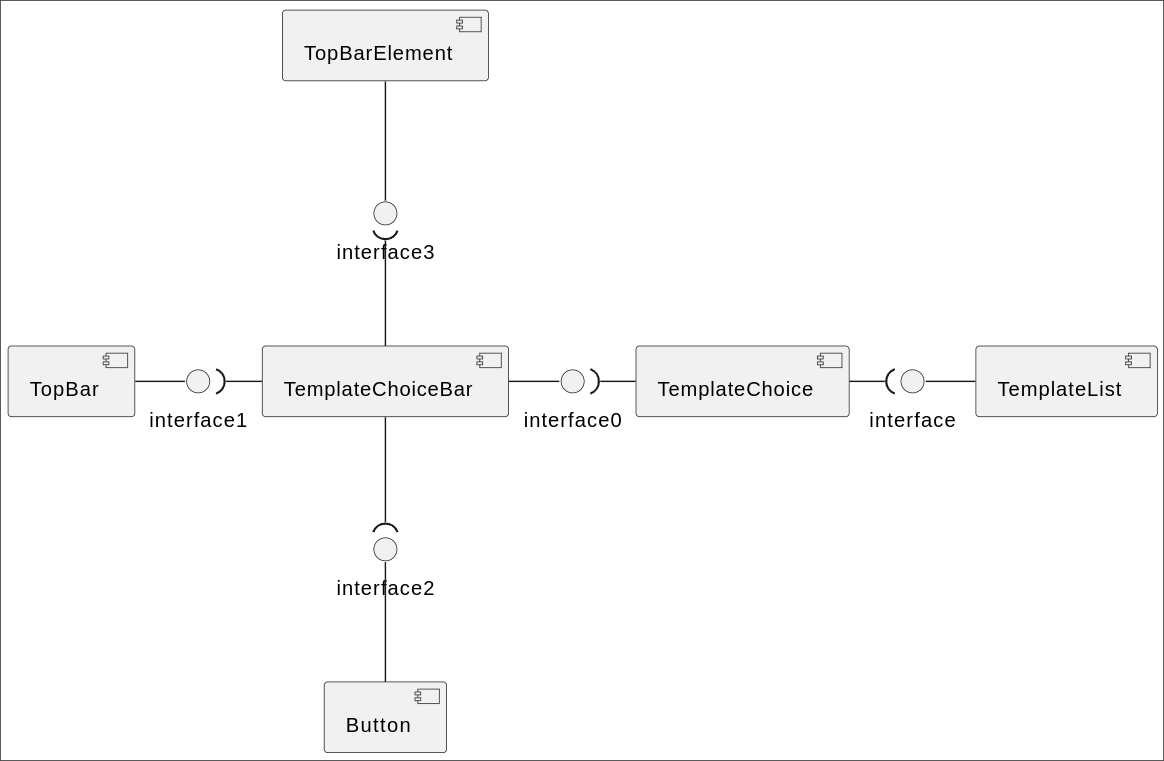
Template Choice Page
-
Dashboard Page
Dynamic View
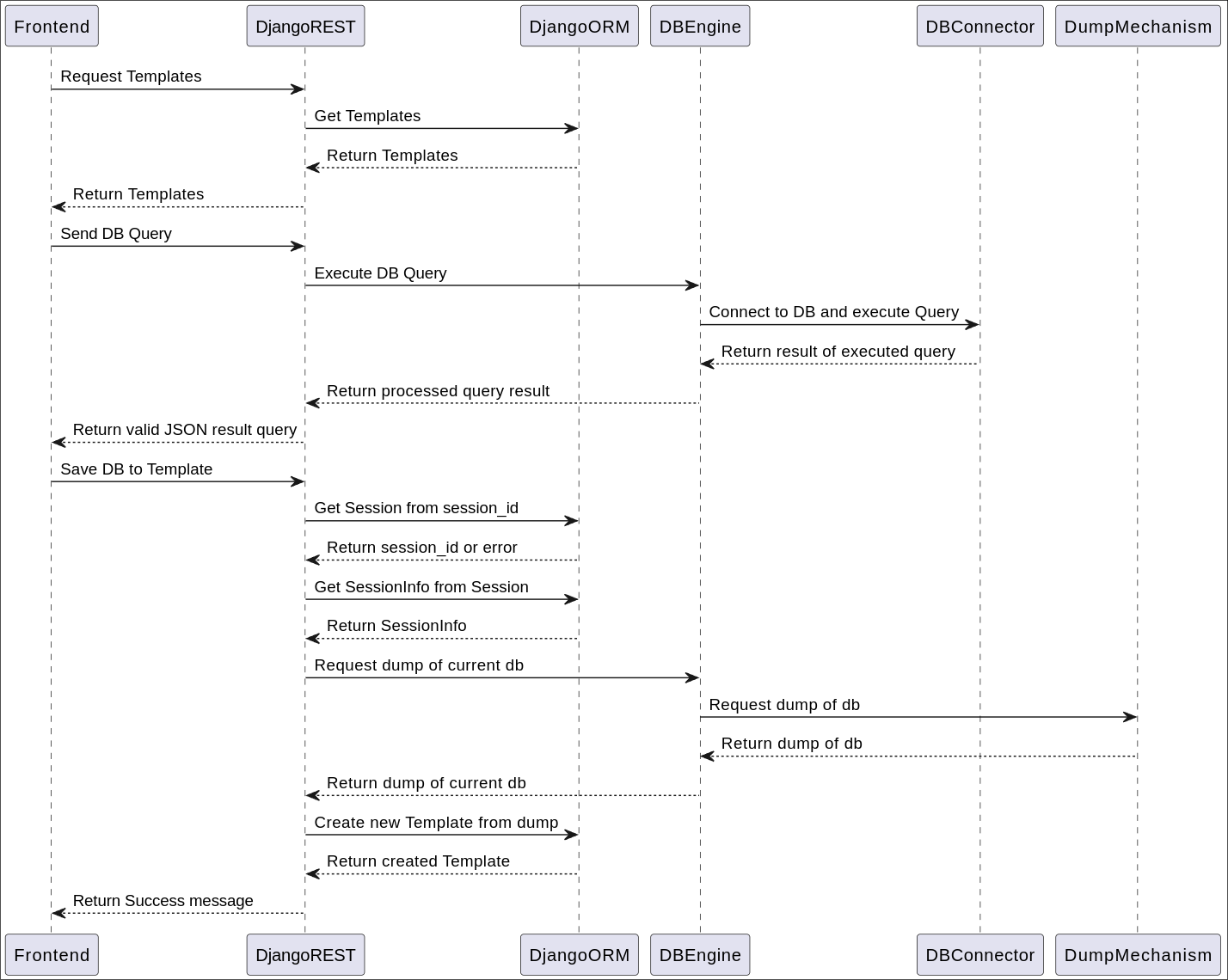
Sequence Diagram of Main Backend Workflows
These scenarios executes almost instantly, as each of them is mostly IO bound tasks
Deployment View